
0. Review
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (1) — Hello Solana
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (2) — Calling Between Programs
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (3) — Program Upgrade
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (4) — Account Validation
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (5) — Multi-Sig
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (6) — Multi-Sig2
1. Overview
In the previous blog, we introduced the implementation of a general Multi-Sig. In this post, we will discuss another security issue — Type Confusion.
2. Deserialization/Serialization
In Solana, the program states are stored in accounts. The type confusion issue arises during the deserialization/serialization of accounts. The logic of the program usually rely on the data structures. However, the program may not check the type of the accounts properly during the deserialization/serialization process. This may be abused by attackers, resulting in unexpected loss.
3. Code Review (Type Confusion)
In the following, we illustrate the issue of type confusion with a simple program. You can find the test code here.
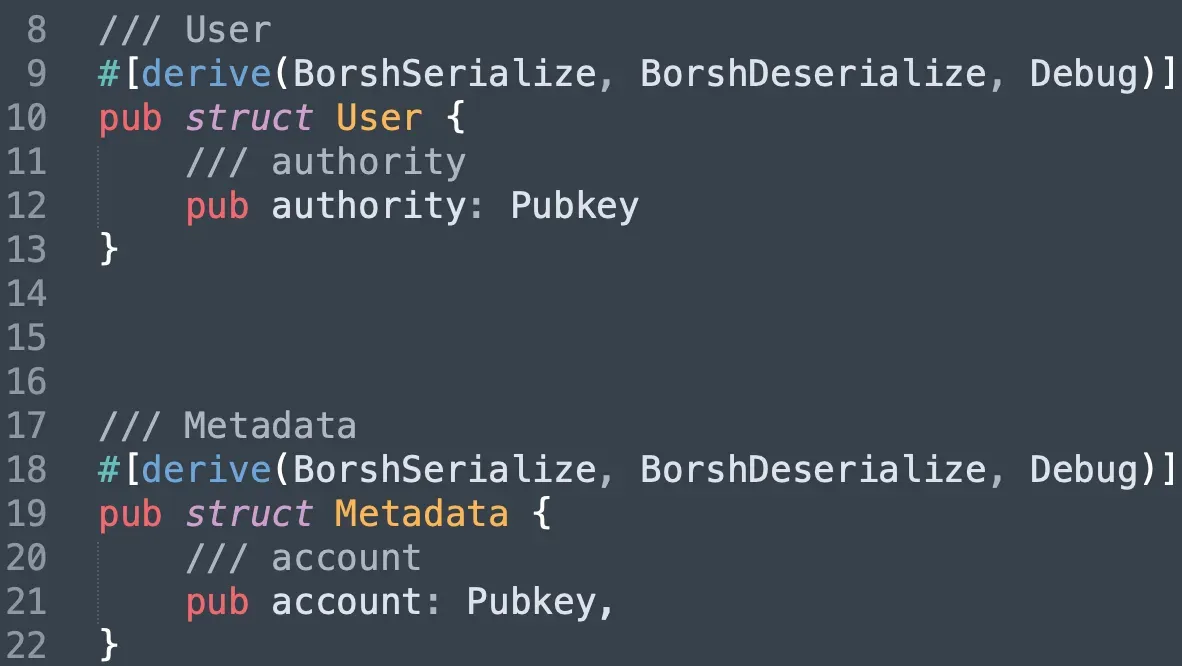
In the test program, we implement two data structs, one is User and the other is Metadata. Both of them record the public key of an account (different account).
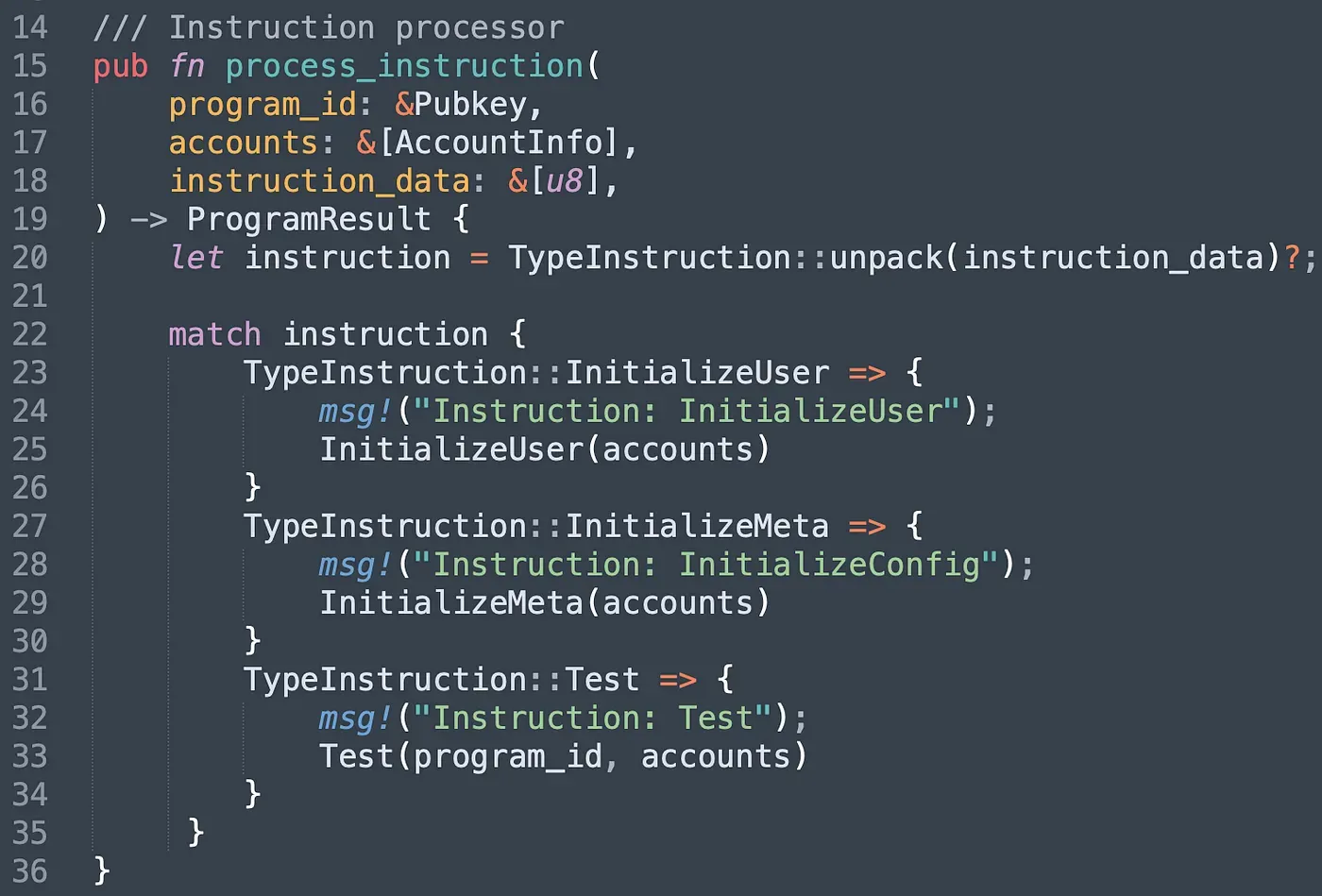
The program has three different instructions. Instruction InitializeUser is designed for creating the User account and setting an authorized account (i.e., authority). Similarly, instruction InitializeMeta is invoked for creating the MetaData account and setting a normal account (i.e., account). Instruction Test demonstrates that the attacker can bypass the verification logic of the program and conduct attacks with controlled MetaData.
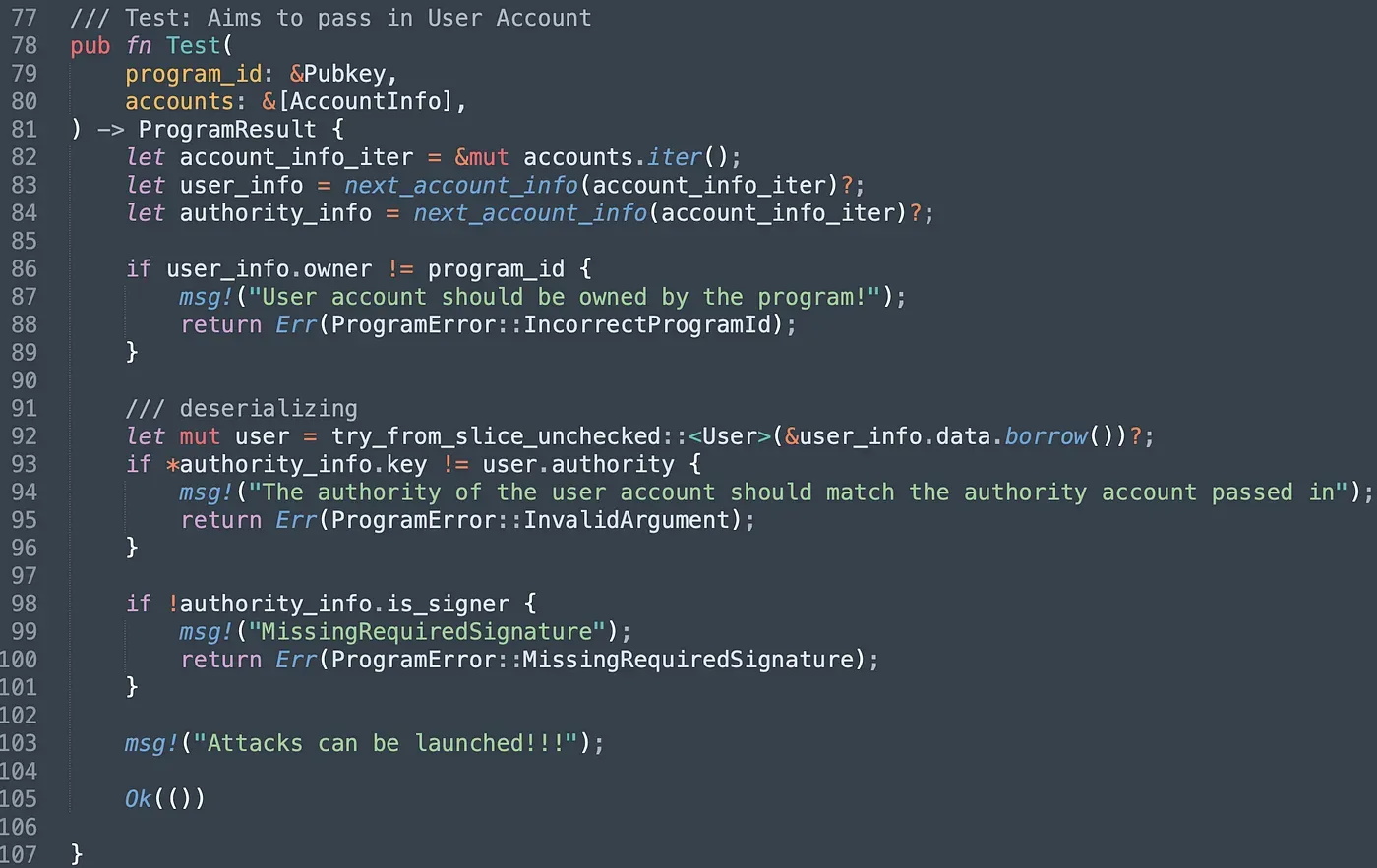
Let’s walk through the instruction Test(). The program ensures the owner of the User account passed in is the program itself (line 86 - line 89). After deserialization (line 92), the program compares the public key of the authority account passed in with the public key stored in the User account. If they are not equal, the program reverts (line 93 - line96). The last check is to ensure the authority account has signed the transaction. However, if an attacker pass in the controlled Metadata account, all the check can still be bypassed. The reason is that the program doesn't check the type of accounts. It receives an array of bytes and deserializes it directly into different types of structs defined in the program.
We deploy the test program for the further test, and it can be found in this link.
3.1 Send Transaction
After deploying the program, we write the script to invoke three instructions provided in the program in order.
We first invoke the InitializeUser and InitializeMeta. Note that we set our own public key as the account account stored in the Metadata account.
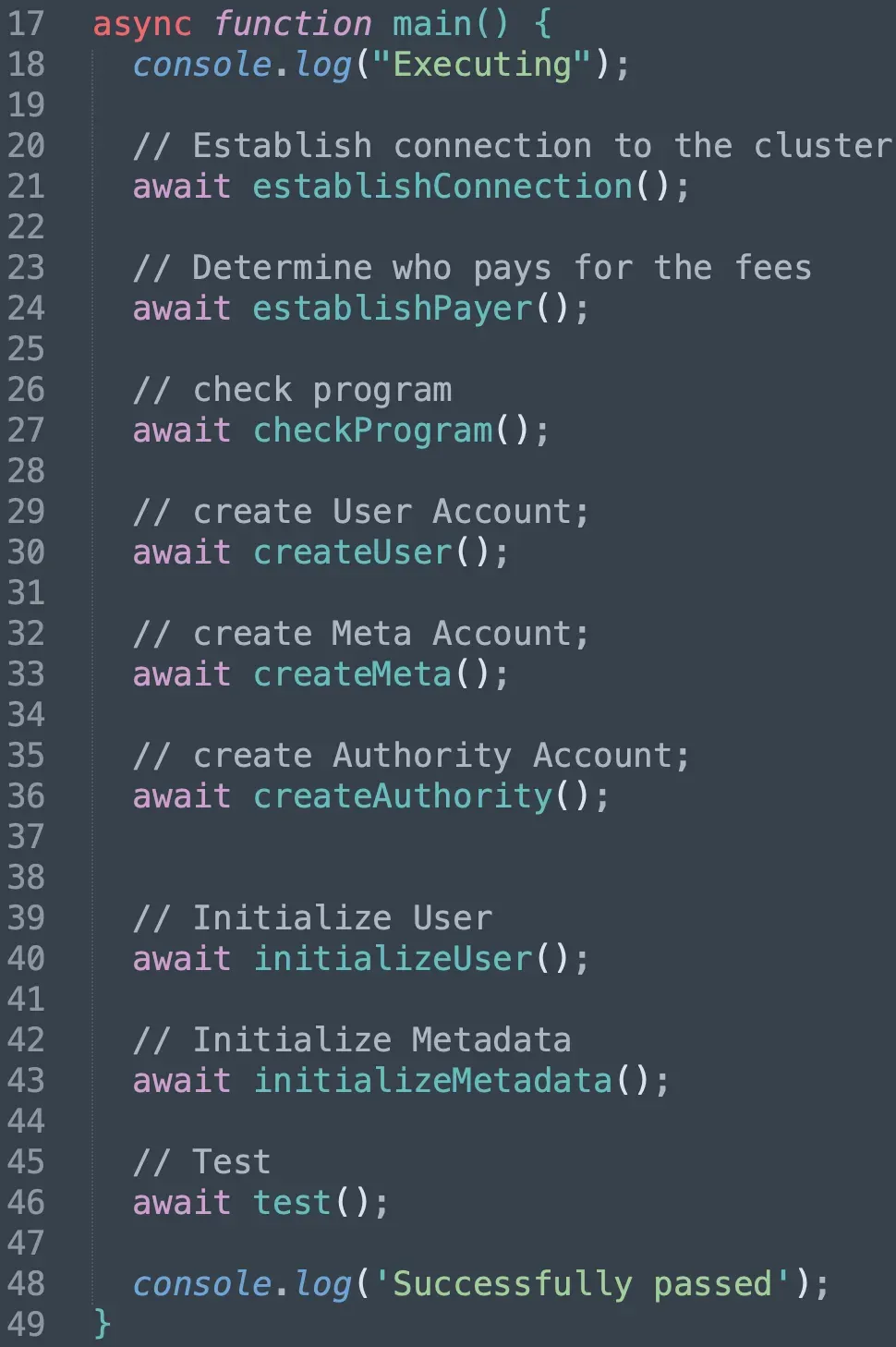
In function test(), we pass in the Metadata account as the User account and our own account as the authority_info (line 347 - line 348). The program de-serialized the Metadata with struct User and all the check can be bypassed.
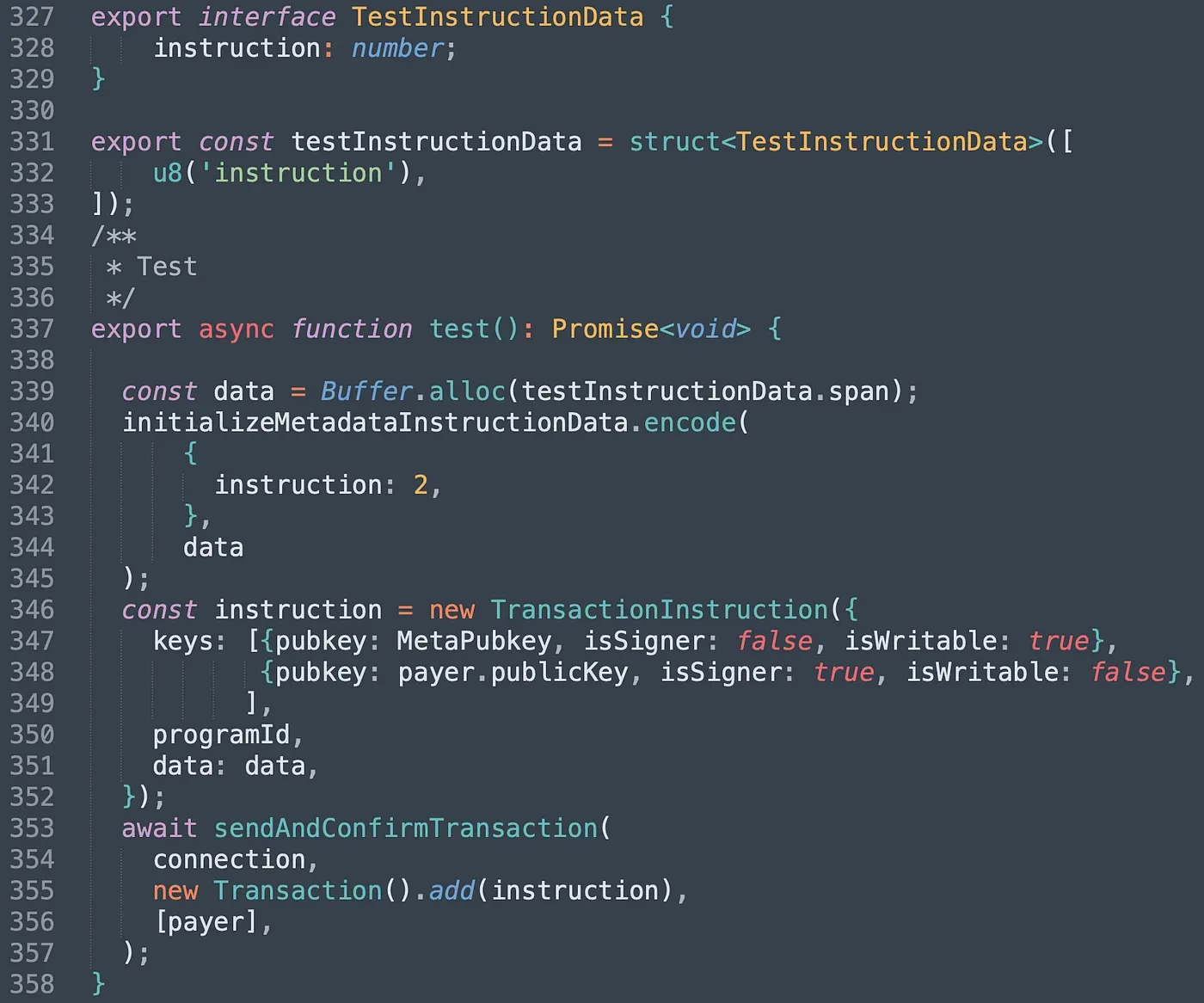
We send the transaction and it can be found here. The program returned success, which means we successfully passed the check with the unchecked account type.
4. Summary
In this article, we introduce the problem of type confusion in Solana. There are many ways to avoid this problem. For example, we can add one attribute to record the type of the account in the struct, and the program should always check the type attribute before reading/writing from/to the account passed in. Keep following, and we will share more in the upcoming posts.
Read other articles in this series:
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (1) — Hello Solana
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (2) — Calling Between Programs
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (3) — Program Upgrade
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (4) — Account Validation
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (5) — Multi-Sig
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (6) — Multi-Sig2
About BlockSec
BlockSec is a pioneering blockchain security company established in 2021 by a group of globally distinguished security experts. The company is committed to enhancing security and usability for the emerging Web3 world in order to facilitate its mass adoption. To this end, BlockSec provides smart contract and EVM chain security auditing services, the Phalcon platform for security development and blocking threats proactively, the MetaSleuth platform for fund tracking and investigation, and MetaSuites extension for web3 builders surfing efficiently in the crypto world.
To date, the company has served over 300 esteemed clients such as MetaMask, Uniswap Foundation, Compound, Forta, and PancakeSwap, and received tens of millions of US dollars in two rounds of financing from preeminent investors, including Matrix Partners, Vitalbridge Capital, and Fenbushi Capital.
Official website: https://blocksec.com/
Official Twitter account: https://twitter.com/BlockSecTeam




