
0. Review
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (1) — Hello Solana
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (2) — Calling Between Programs
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (3) — Program Upgrade
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (4) — Account Validation
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (5) — Multi-Sig
1. Overview
In the previous post, we discussed the implementation of the Multi-Sig. However, the implementation assumes that the signatures from multiple users can be collected at the same time off-chain. In this post, we introduce a more general Multi-sig program that allows users to sign fully on-chain.
2. Design Of Test Program
The multi-sig program allows valid signers to sign the proposer in separate and anyone can execute the proposer once it is approved (enough signatures are collected). All the test code can be found here.
3. Code Review
This program introduces two more structs and they are TransactionAccount and Transaction. Struct TransactionAccount is designed for recording the account information used for the proposed transaction. Struct Transaction is used to record the information of a proposal. Note that the attribute signers is used to record the number of valid signatures. did_execute and is_initialized ensure the execution and the initialization can only be done once.
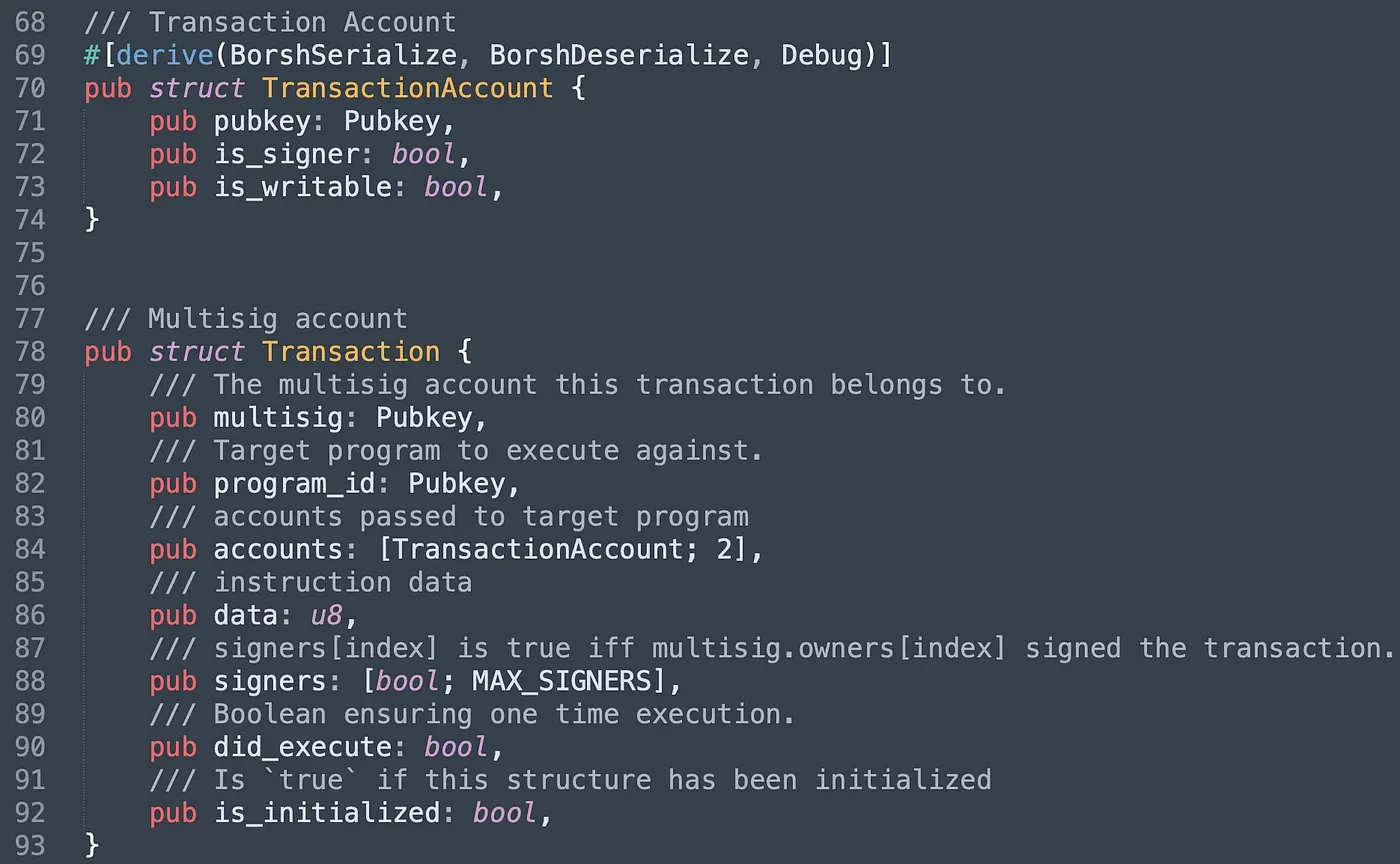
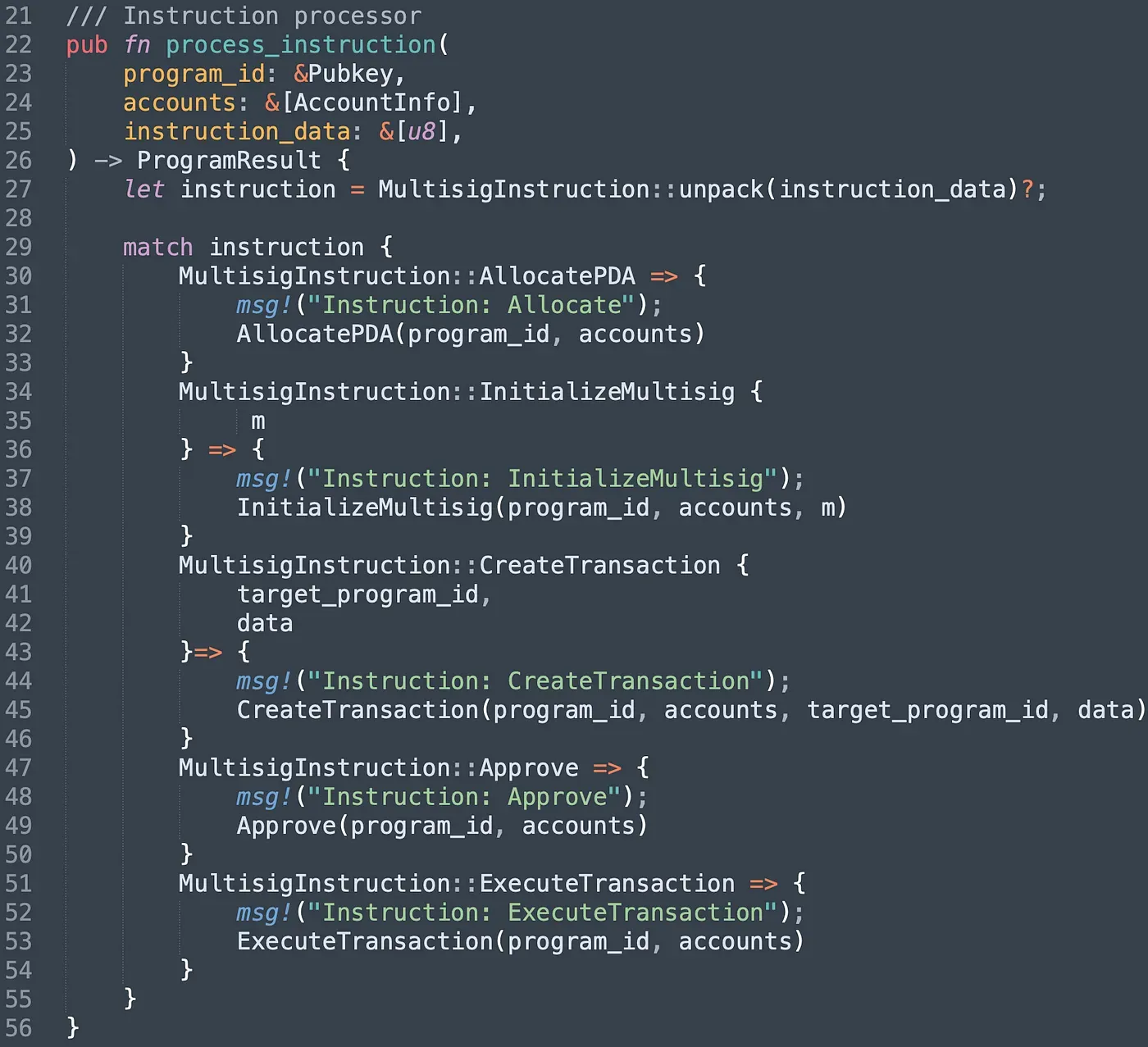
The program provides five different instructions. Instruction AllocatePDA aims to create a unique PDA account, and uses it as the multisig account. It will record all the valid signers' information. In instruction InitializeMultisig, we set the number of signatures required to execute the instruction, and the array of valid signers' public keys as well. Instruction CreateTransaction is used to create a proposal while signer can approve the proposal via the instruction approve. Once the number of the approval reaches the threshold set in multisig, the instruction ExecuteTransaction can be invoked to execute the transaction.
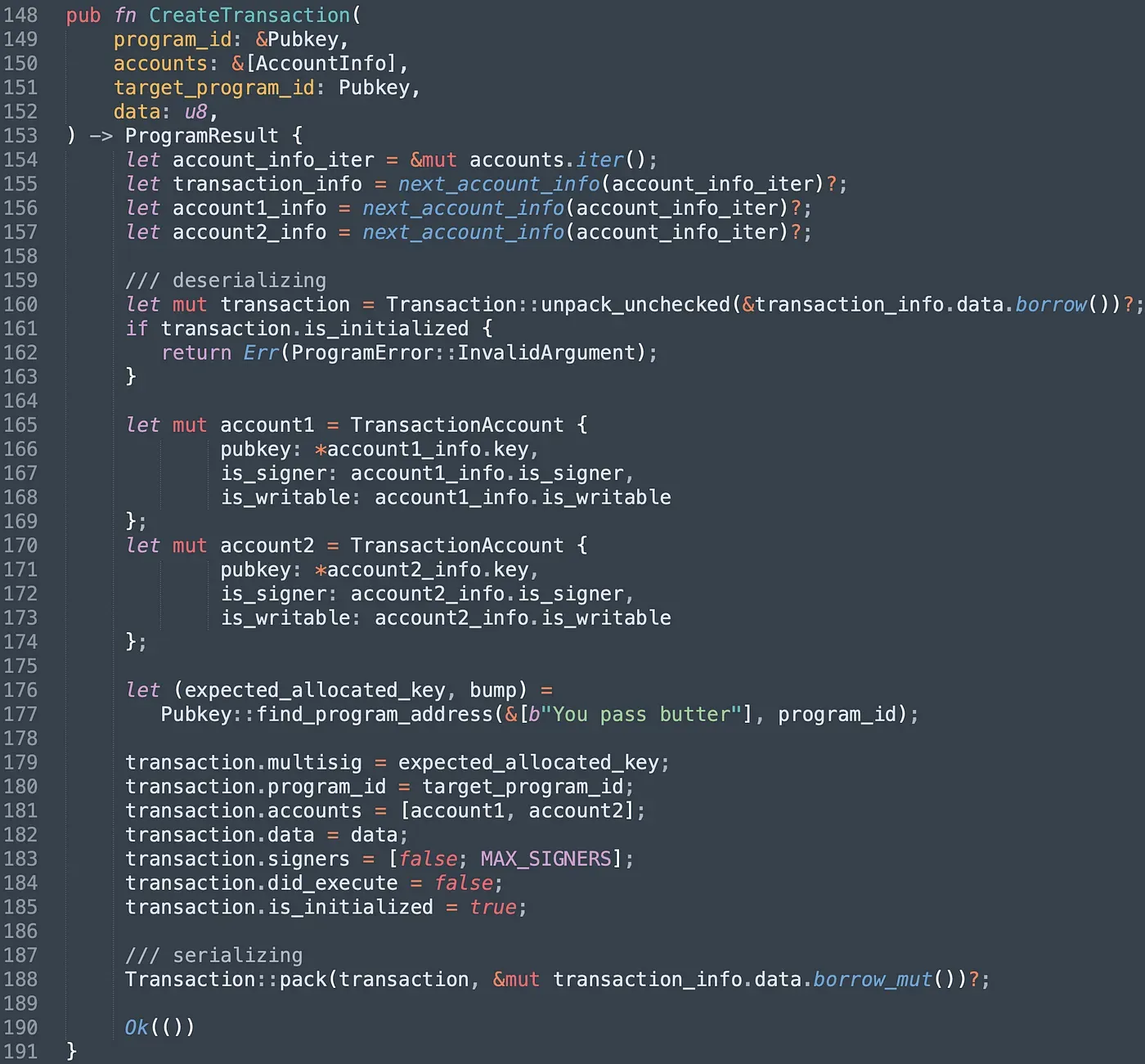
To submit a proposal, users can invoke the instruction createTransaction(). It takes three accounts, which are created transaction account, the next two accounts are used by the target transaction. To prevent the account from being re-initialized by malicious users, we check the attribute is_initialized (line 161-163). After that, we init the struct TransactionAccount with specified data and serialize it into the data account(line 188).
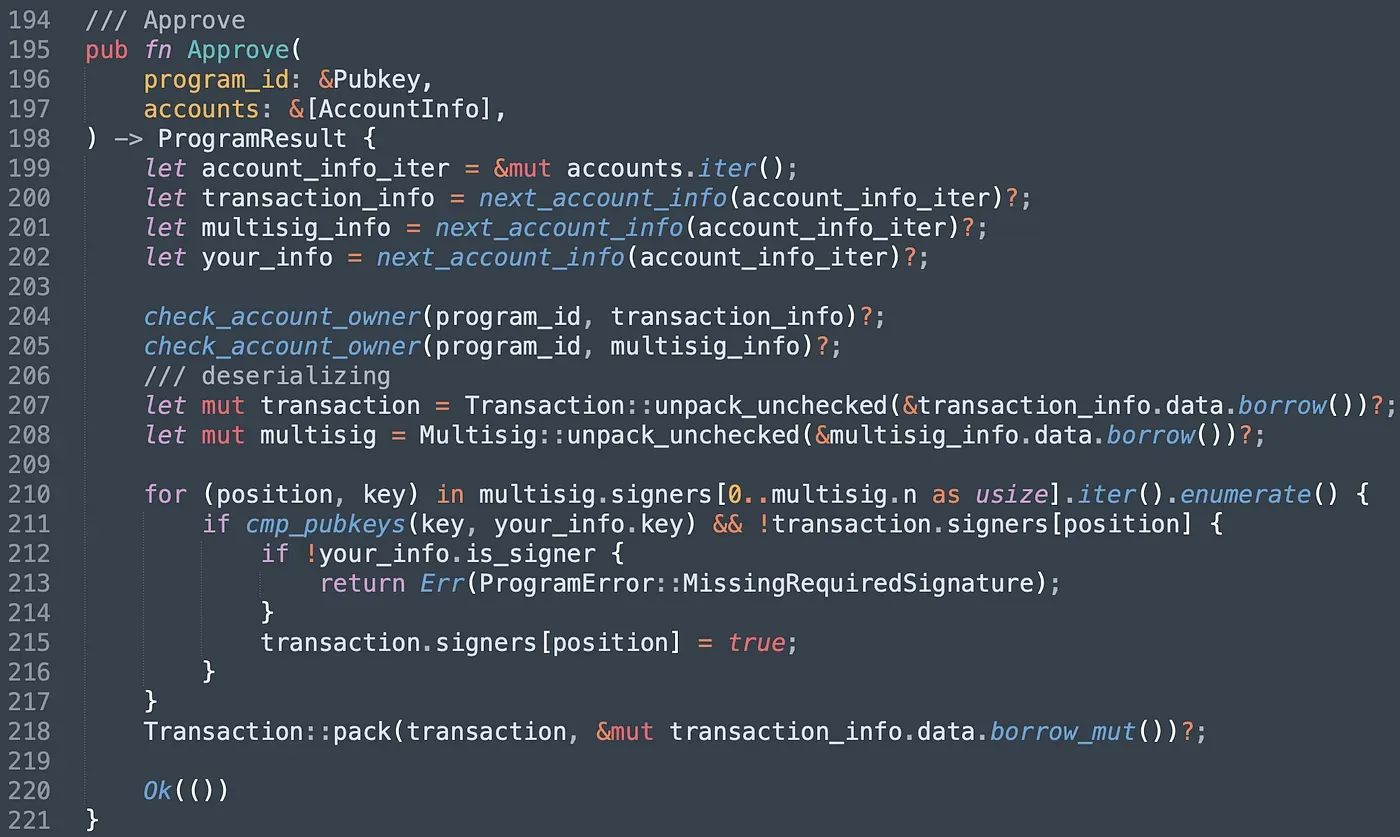
In function Approve(), we first check whether the Transaction account and the multisig account are owned by the program. Note that accounts created from other programs may be used by malicious users here if there is no check. Next, we match the pubkey of the signer with the keys stored in multisig account. If matched, it will validate your signature, and change the value to true correspondingly.
In instruction ExecuteTransaction(), we count the number of valid signatures. If the number doesn't reach the threshold, the program will revert.
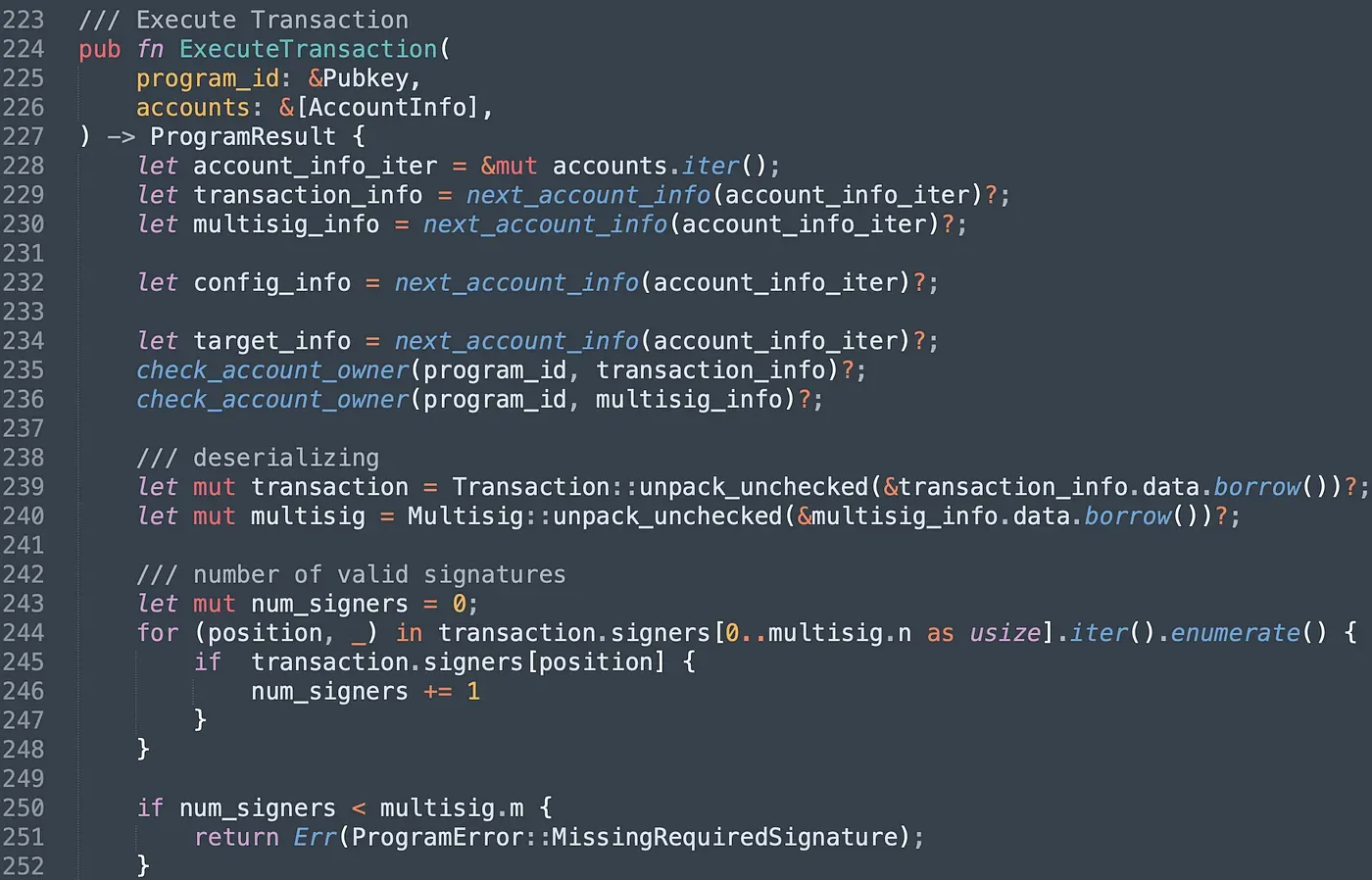
After that, we init the target Instruction with specified attributes and invoke the instruction of the target program via the function invoke_signed(). We finally set the attribute did_execute to true in case the proposal is executed repeatedly.
We deployed the program on testnet and it can be find in the following link.
https://explorer.solana.com/address/CPzn7ptnJntjUB4NGKqQGRai8NFLNwFaspmJ7nEGbMHe?cluster=testnet
4. Send Transaction
After the deployment, we create the multisig account first and set the multisig account as the admin of the config account when initialize the config account. Related transactions are shown below, and the order is: createMultisig() (in General-Multisig) -> Deploy PriviligeOwner program -> Allocate() (in PrivligeOwner) -> InitializeConfig() (in PrivligeOwner).
https://explorer.solana.com/tx/2vXHmwbCsARstx8wi4eLACbrb6PuZZMktsqU8VnJLp64fvrpaE62QSTn5QLczzxnTvxRLWMSR3dKLGYXZasGMn69?cluster=testnet
https://explorer.solana.com/tx/2EMq9y6HNnXq1n2XsqrBkJd8RGL27PCj5T4JyJ71ZoA3ipUggT6dF6S6uDv4TtxGGKk8BmiAJHS7BFRgZqWjkWVb?cluster=testnet
https://explorer.solana.com/tx/3UhXKsTubUiPqRtLyNYskxvbyrTKHsbeptxuAfJQ348AU4b8gQET2HAMaqxwud6Wo3MKTYHWBneqa9z2WhCpwV6t?cluster=testnet
https://explorer.solana.com/tx/5NA7Yw23uRf48Q3BYM21dtS7gD9YMECij43ZaRLMPe7svt3bsv2TPWwbCRP5akDmttjLEHWZtpqrZrVLNr9QLyJY?cluster=testnet
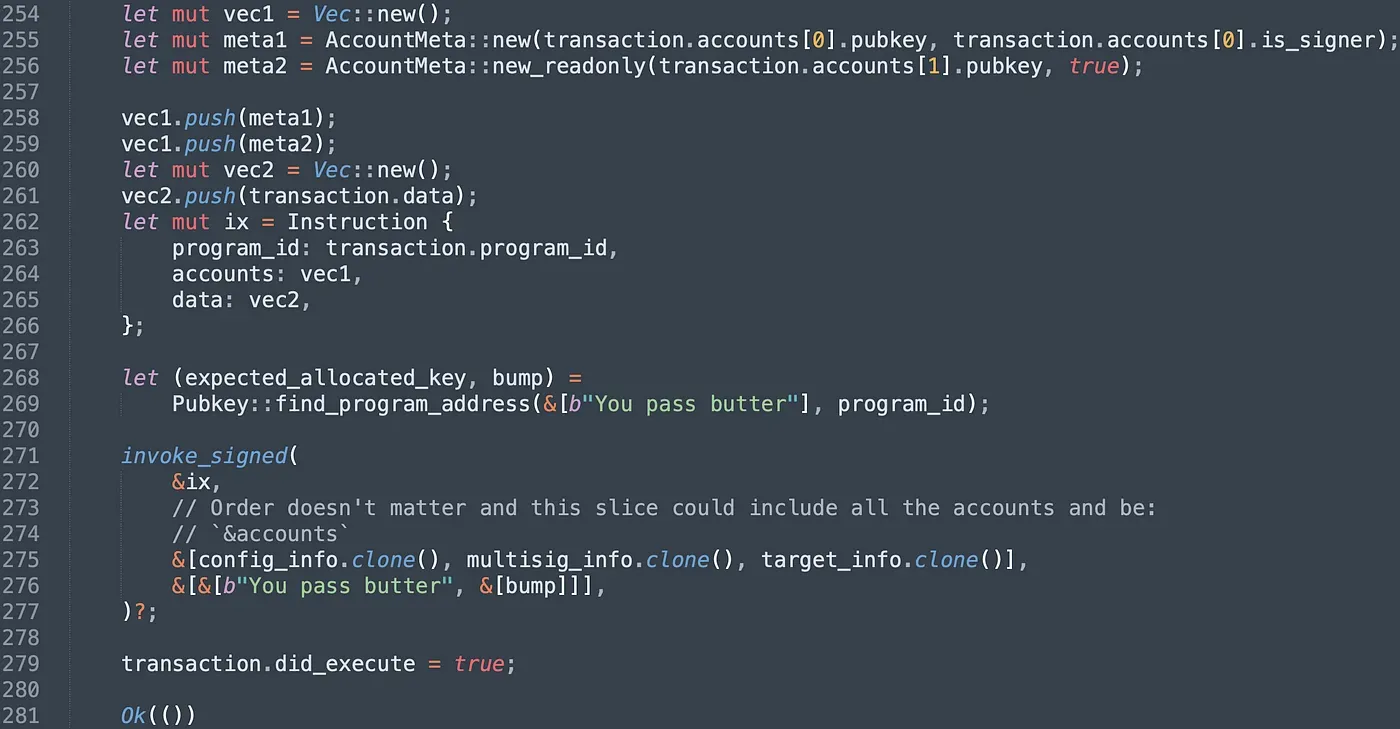
Next, we invoke instruction InitializeMultisig(). We pass in four accounts and they are the multisig account and three valid signer's accounts. We set the value of m to 2, which means two of the three signers' signatures is required to execute privilege functions.
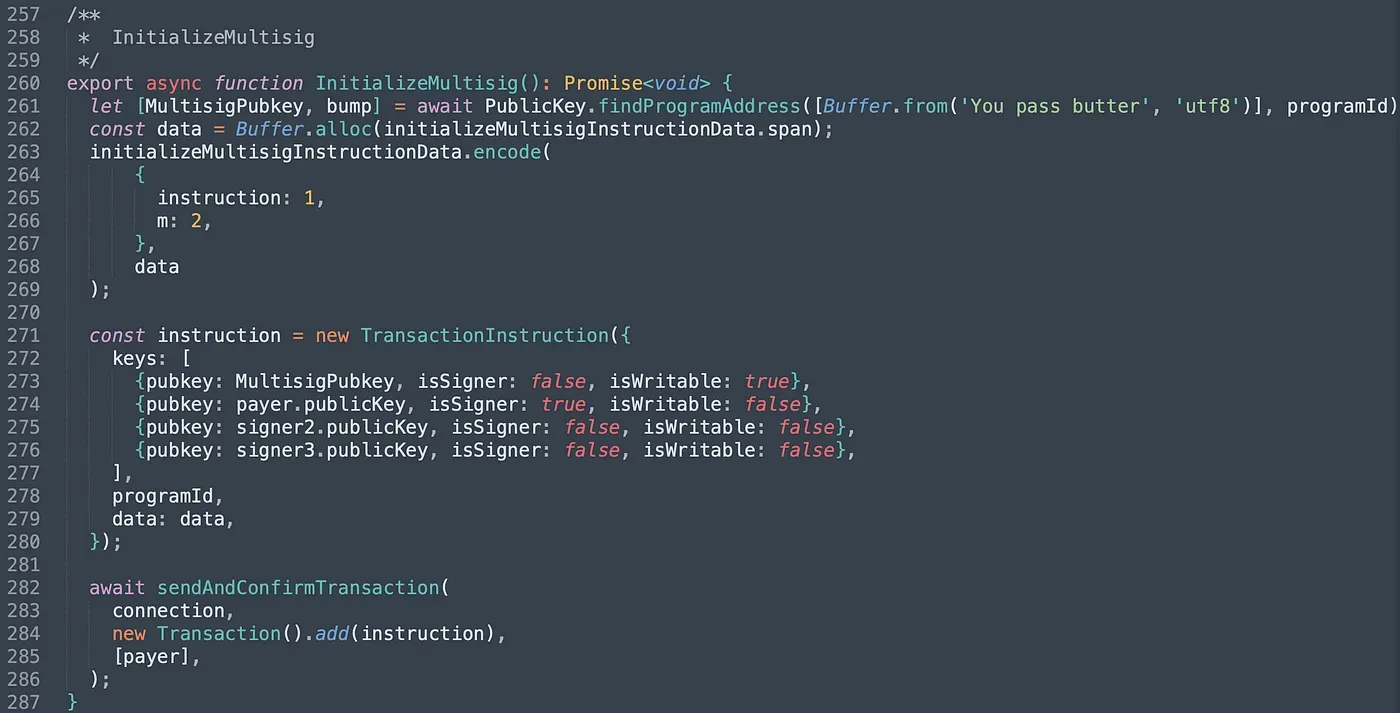
In function CreateTransaction(), we pass in the created Transaction account, the pubkey of the target program (PrivilegeOwner) and the pubkey of the config account (line 306 -line 307). Besides, we should also set the _data to 3, which corresponds to the instruction unlock() in PrivilegeOwner program.
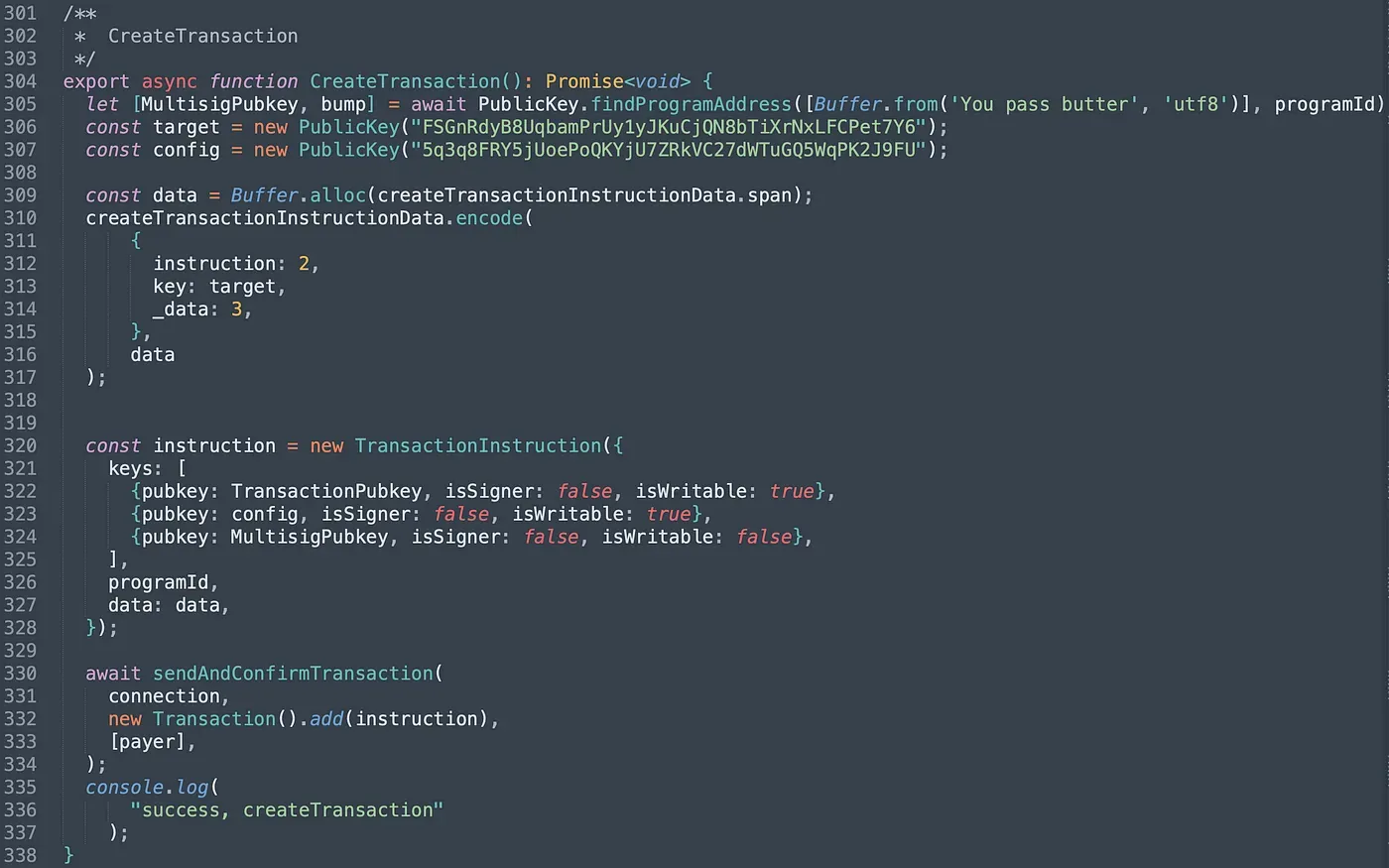
For the first test, only one signer approves the created proposal. In this case, ExecuteTransaction() fails as limited signatures are collected. The console prints the following output.
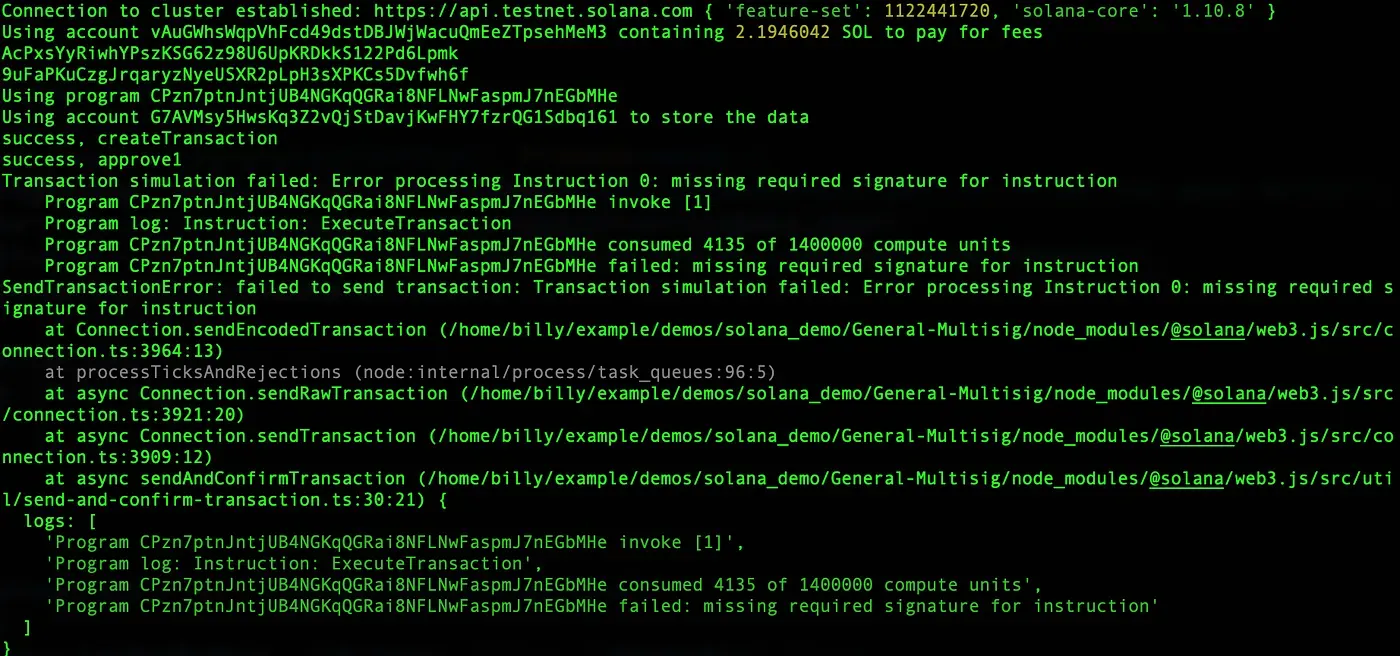
Another signer approves the created proposal and invokes ExecuteTransaction(). The total number of signatures has reached to the threshold so that the proposal can be executed successfully.
https://explorer.solana.com/tx/55Qy93RxybsT7c5v9AFgN8Dt1h3AVJfbsosLbstYVB6paY1wmau5sdtLfGpfryXnZTsBNRauvwLSmAu2nABFxVCe?cluster=testnet
https://explorer.solana.com/tx/4XF4MUhL4oftkDt4sn7NoREmGqcDMVP6HGypvJQMtiAbBKiCuy4B98vhQKtvm4mPv7SprrDDVsiwgb6pNwgJcTwz?cluster=testnet
4. Summary
In this article, we introduce the general implementation of the multisig in Solana. The implementation makes use of the feature of PDA, which enables the program to sign the transaction by PDA automatically when the number of valid signatures meets the requirement. Keep following, and we will share more in the upcoming posts.
Read other articles in this series:
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (1) — Hello Solana
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (2) — Calling Between Programs
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (3) — Program Upgrade
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (4) — Account Validation
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (5) — Multi-Sig
- Secure the Solana Ecosystem (7) — Type Confusion
About BlockSec
BlockSec is a pioneering blockchain security company established in 2021 by a group of globally distinguished security experts. The company is committed to enhancing security and usability for the emerging Web3 world in order to facilitate its mass adoption. To this end, BlockSec provides smart contract and EVM chain security auditing services, the Phalcon platform for security development and blocking threats proactively, the MetaSleuth platform for fund tracking and investigation, and MetaSuites extension for web3 builders surfing efficiently in the crypto world.
To date, the company has served over 300 esteemed clients such as MetaMask, Uniswap Foundation, Compound, Forta, and PancakeSwap, and received tens of millions of US dollars in two rounds of financing from preeminent investors, including Matrix Partners, Vitalbridge Capital, and Fenbushi Capital.
Official website: https://blocksec.com/
Official Twitter account: https://twitter.com/BlockSecTeam




