Starting a crypto payment business in Canada in early 2026 is bold. However, many founders don’t realize they are on shaky ground. You likely believe that securing your Canada MSB (Money Services Business) registration number is the finish line—the "golden ticket" that unlocks banking and market access. However, the reality of the 2026 regulatory landscape is far more brutal.
Since the recent tightening of FINTRAC enforcement and the expanded scope of the Retail Payment Activities Act (RPAA), simply "having a license" is no longer a defense. Banks are closing accounts of registered MSBs quickly. This isn’t due to a lack of license. Instead, it’s because their post-registration compliance is weak. Without real-time tracking, one risky USDT transfer can trigger an AML freeze. This could halt your whole operation and result in heavy penalties.
To thrive in 2026, shift from a "registration-first" approach to an "infrastructure-first" strategy. This guide moves beyond the paperwork. We outline the steps to secure your MSB status. More importantly, we show how to create a blockchain-native compliance engine that meets FINTRAC’s 2026 standards. From automated Travel Rule protocols to real-time KYT (Know Your Transaction), here is how you build a crypto payment business that lasts.
What Is a Canada MSB License?
Defining the Money Services Business in Web3
A Money Services Business (MSB) license in Canada is not a discretionary "permission slip" like a banking charter. Instead, it is a mandatory registration status for any business that deals with funds or virtual currency. Whether you run a crypto exchange, a payment gateway, or a remittance service, you are acting as a financial intermediary.
In the eyes of the law, if you touch customer funds or facilitate the movement of value, you are an MSB. This registration shows the government and banks that you are a legal business. It removes the "shadowy" stigma often associated with crypto startups and places you in a regulated framework.
The Role of FINTRAC
The group that oversees this area is FINTRAC, the Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre of Canada. FINTRAC isn't a police force. It's a financial intelligence unit. Its main job is to detect and prevent money laundering and terrorist financing. When you register as an MSB, you are essentially entering a partnership with FINTRAC. You agree to watch for bad actors on your platform. If you report any suspicious activity, you can operate legally in Canada.
Who Needs an MSB License in Canada for Crypto?
Activities That Trigger Registration
Determining if you need to register can sometimes be confusing for innovative Web3 models. However, the rule of thumb is generally based on "custody" and "exchange." If your business model involves exchanging fiat currency for virtual currency (like Bitcoin or USDT), or exchanging one virtual currency for another, you must register.
Also, you fall under these rules if you transfer virtual currency for a client. This includes a payroll provider paying staff in crypto or a remittance platform sending funds across borders. If you are a foreign company offering services to Canadian customers, you must register as a Foreign Money Services Business (FMSB).
The Nuance of Non-Custodial Services
The lines get blurrier with non-custodial DeFi protocols or software developers. generally, if you never hold the private keys and never take possession of customer funds, you might not be classified as an MSB. However, if you provide a user interface that simplifies these transactions and you collect fees in a way that resembles a financial service, regulators may take a closer look. It is always safer to consult with legal experts, as blockchain regulatory compliance definitions are evolving rapidly.
Benefits of Getting a Canada MSB License
Obtaining your MSB registration is more than just a legal requirement; it is a strategic asset. The primary benefit is access to traditional banking. Canadian banks are notoriously risk-averse regarding cryptocurrency. They will usually refuse to open accounts for crypto companies that can't show they are registered with FINTRAC. The license acts as a badge of legitimacy that opens doors to fiat payment rails.
Additionally, a Canada MSB license is respected globally. Canada has a reputation for strict financial enforcement. This registration makes it easier to partner with liquidity providers. It also helps connect with institutional clients in other regions. It signals to the market that your platform has invested in serious infrastructure and is not a fly-by-night operation.
The Mandatory Architecture of a 2026 Compliance Program
Appointing a Qualified Compliance Officer
In 2026, the role of the Compliance Officer has evolved from a clerical position to a technical one. FINTRAC now expects this individual to possess a deep understanding of blockchain forensics. They are legally in charge of the compliance program. They should explain your transaction monitoring logic during an audit. In 2026, having a figurehead can be a problem for teams. You need someone who can understand on-chain risk scores and handle the reporting lifecycle.
Developing the Five Pillars of Compliance
A robust program must be built on five mandatory pillars: a designated compliance officer, a comprehensive set of written policies, regular staff training, a documented risk assessment, and an independent effectiveness review. In 2026, the "Risk Assessment" pillar is where most crypto MSBs fail. FINTRAC now expects you to go beyond customer demographics and assess geographic risk, product risk, and delivery channel risk specifically as they relate to blockchain vulnerabilities like mixers and cross-chain bridges.
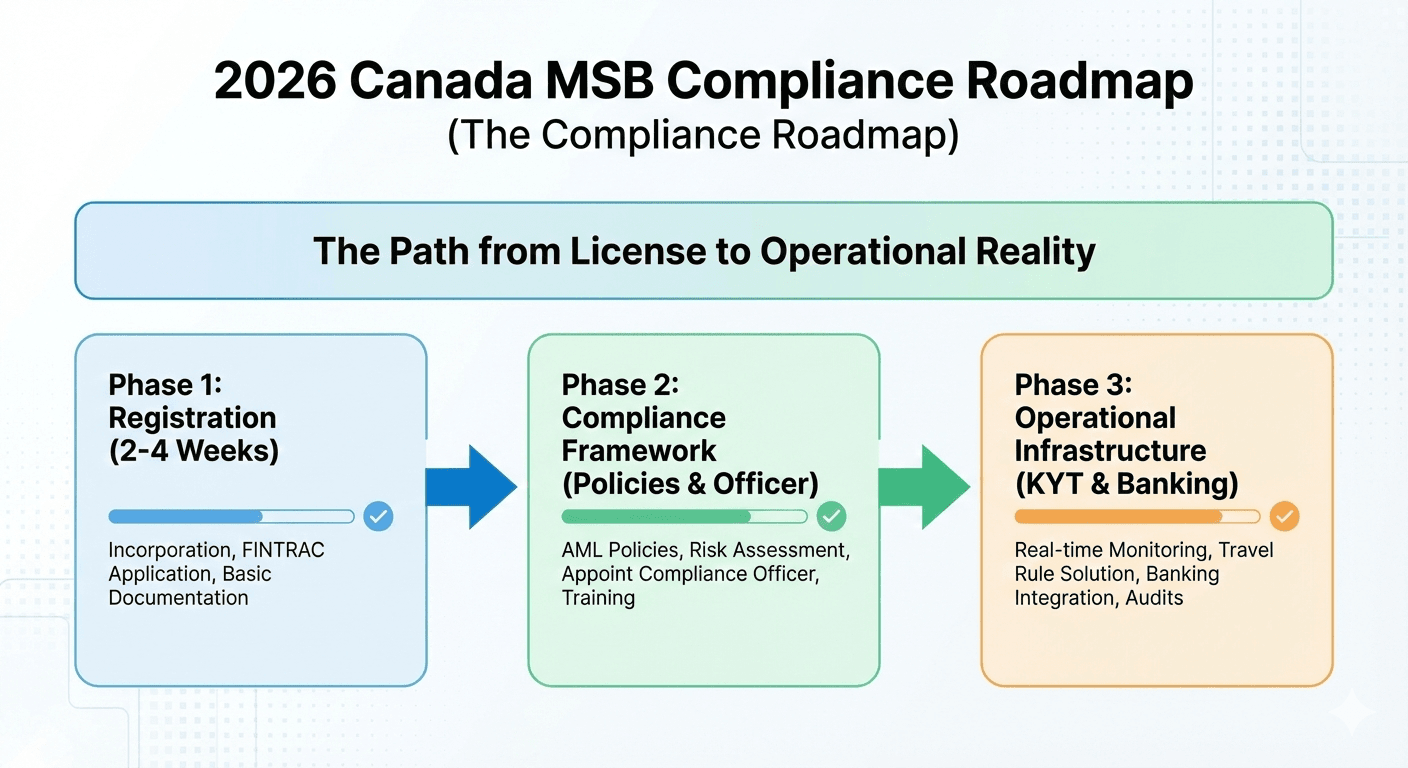
How to Register as a Crypto MSB in Canada (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Corporate Incorporation and Setup
Before approaching FINTRAC, you must exist as a legal entity. You need to incorporate your business either federally or at the provincial level. During this stage, you must also appoint a Compliance Officer. This person is legally responsible for the compliance program. Small teams often have the CEO take on this role. It’s a serious job. Ignoring regulations can lead to personal liability.
Step 2: The Pre-Registration Compliance Framework
This is the step most founders underestimate. You cannot simply register and then figure out your compliance rules later. FINTRAC expects you to have a written AML compliance program ready before you begin operations. This includes clear policies. You will verify customer IDs (KYC). You will assess risk. You will also detect suspicious transactions. If FINTRAC asks to see these documents a week after you register, you must have them ready.
Step 3: Submitting the Application to FINTRAC
Once your entity is formed and your policies are drafted, you can submit your application through the FINTRAC online portal. You need to share details about your bank accounts, your compliance officer, the number of employees, and the types of virtual currencies you plan to support.
Canada reviews applications more efficiently than some places, which can take years. If your paperwork is in order, the registration process can often be completed in a matter of weeks. However, remember that "registered" does not mean "approved." It simply means you are on the list and are now fair game for an audit.
What Happens After You Get the License?
The Myth of "Done"
Many entrepreneurs celebrate once they receive their MSB registration number. This is a mistake. The registration is merely the starting gun. Once you are active, you are under constant scrutiny. The law says you must keep records and verify identities. You also have to report certain types of transactions within strict time limits.
Ongoing Reporting Obligations
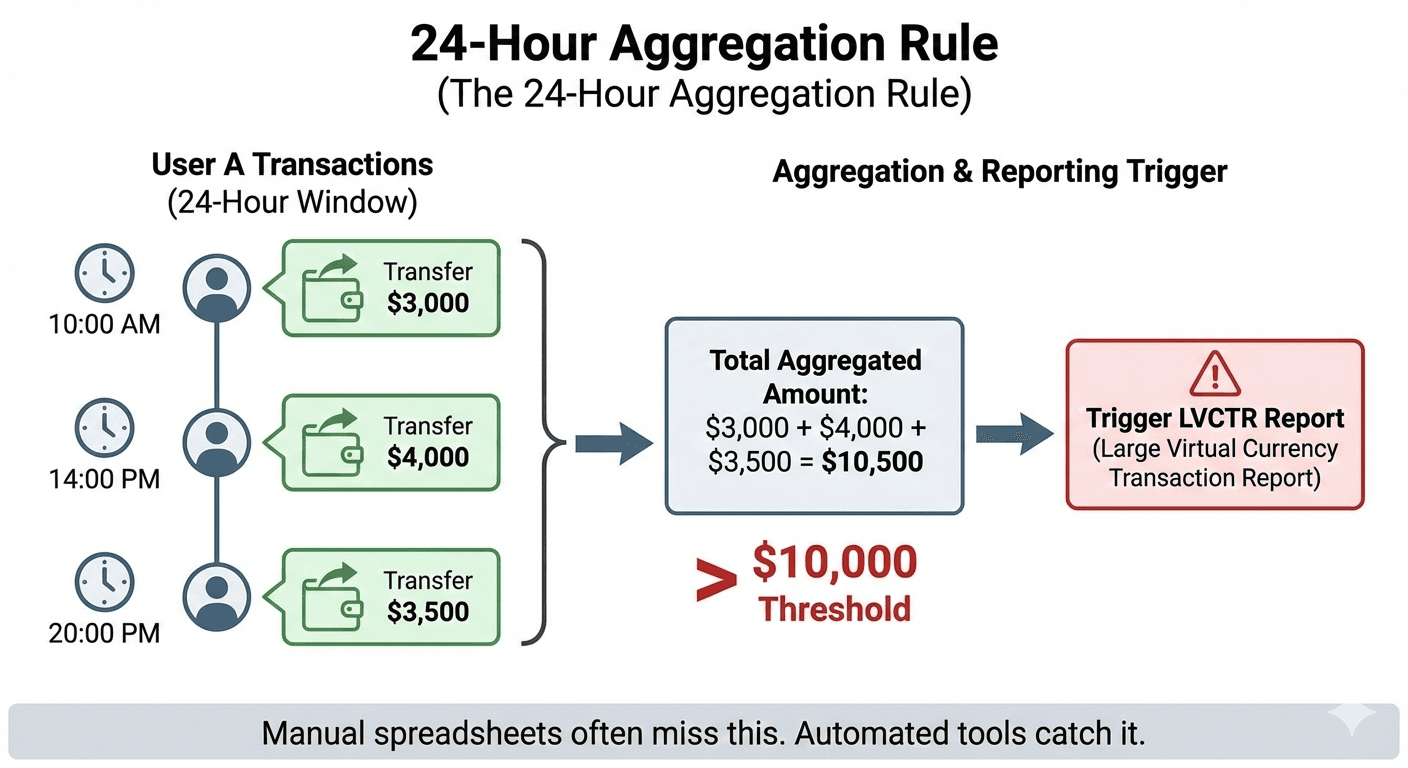
You must submit reports to FINTRAC under several specific circumstances. For example, any cash transaction of $10,000 or more must be reported. Crypto companies must report any receipt of virtual currency worth $10,000 or more in one transaction. If you spot a suspicious transaction—no matter how much—it’s important to file a Suspicious Transaction Report (STR). Missing these deadlines can result in severe fines.
Canada MSB AML Requirements for Crypto Companies
Customer Identification and KYC
The foundation of your compliance program is knowing who your users are. You cannot allow anonymous trading. You need a strong Know Your Customer (KYC) process. This checks government-issued IDs against selfies or liveliness tests. This data must be stored securely and updated regularly.
The Critical Role of KYT (Know Your Transaction)
In the world of crypto, knowing who the customer is isn't enough; you must know where the money is coming from. This is where Know Your Transaction (KYT) comes into play. Crypto uses public blockchains. Traditional banking relies on closed networks. You must ensure that Bitcoin or USDT coming into your platform isn’t tied to hacks, ransomware, or sanctioned groups.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
You are required to assess every business relationship for risk. A customer who transfers small amounts locally has a different risk profile than a user who moves large sums to a high-risk jurisdiction. Your compliance program must be dynamic. It needs to flag high-risk activities automatically so your compliance officer can review them. This "risk-based approach" is the core standard that FINTRAC auditors look for.
Why Many Crypto MSBs Struggle With Ongoing Compliance
The Manual Process Trap
New MSBs often try to manage compliance using spreadsheets and manual checks. They might manually look up a wallet address on a block explorer to see if it looks safe. This approach fails quickly. Crypto moves 24/7, and the volume of transactions makes manual review impossible. A single missed link to a sanctioned wallet can result in your bank account being closed.
The Complexity of Cross-Chain Crime
Modern financial crime is sophisticated. "Dirty" money rarely stays on one chain. A hacker might steal funds on Ethereum, swap them to a different chain like Tron, and then try to deposit them into your platform. Traditional tools often lose track of the money once it jumps chains. If your monitoring system cannot see across different blockchains, you have a blind spot that criminals will exploit.
How Phalcon Compliance Supports Canada MSB Crypto Companies
To meet Canada's MSB license requirements and keep your business growing, you need automated systems. This is where Phalcon Compliance becomes a critical partner for crypto payment companies.
Real-Time Blockchain Monitoring
Phalcon Compliance offers automated KYT screening that analyzes transactions before they are finalized. It reviews the wallet addresses that have used your platform. It looks for connections to darknet markets, scams, or sanctioned groups. You can block risky deposits right away. This keeps your platform safe from illicit funds.
Comprehensive Cross-Chain Visibility
Phalcon offers extensive support for various assets. It covers major chains such as Ethereum, Tron, BNB Chain, Polygon, Base, Optimism, Avalanche C-Chain, and Arbitrum. It traces funds even as they move across different networks, ensuring that you have a complete picture of the fund's journey. This level of visibility is key for meeting the strict standards of Canadian banking partners.
Audit-Ready Data
When FINTRAC eventually audits your business, they will ask for proof of your monitoring decisions. Phalcon Compliance generates detailed, structured risk reports for every transaction. You can show auditors why a transaction was flagged or approved. This turns a stressful audit into a routine job.
Final Thoughts: License Is Step One. Compliance Is the Real Game.
Acquiring a Canada MSB license is a significant milestone. It validates your business model and allows you to enter the formal economy. However, the license itself does not guarantee success. The long-term viability of your crypto payment business depends entirely on your ability to manage risk.
Regulators and banking partners are no longer impressed by companies that merely have a compliance policy on paper. They demand proof that you can stop money laundering in real-time. Start with advanced blockchain tools like Phalcon Compliance. This choice builds a secure and scalable foundation. It prepares you for success on the global stage. Do not just build a licensed business; build a compliant one that is built to last.
FAQ
- What is a Crypto MSB in Canada and who needs to register?
A Money Services Business (MSB) in Canada is any entity that deals in foreign exchange or virtual currencies. If your business handles crypto-for-fiat or crypto-for-crypto, you need to register with FINTRAC. This also applies if you transfer virtual currency for clients. It includes custodial wallets and payment gateways. This applies to both Canadian companies and foreign companies directing services to Canadians.
- How much does it cost to get a Canada MSB license?
Technically, FINTRAC does not charge a fee to submit the registration form itself. However, the "free" registration is misleading. The real costs involve legal incorporation, drafting a compliant AML program (consulting fees), and purchasing ongoing compliance software (KYT tools). Most crypto startups budget between $5,000 to $20,000 USD for the initial setup and legal structuring.
- Does an MSB license guarantee a Canadian bank account?
No. This is the biggest misconception. An MSB license is a requirement to apply for a bank account, but it does not guarantee one. Canadian banks are strict. They will only open accounts for crypto MSBs that can show they have strong, real-time transaction monitoring (KYT) and AML policies. These measures help detect illicit funds.
- What is the $10,000 rule for crypto transactions in Canada?
Under FINTRAC rules, MSBs must file a Large Virtual Currency Transaction Report (LVCTR) for any receipt of virtual currency equivalent to $10,000 CAD or more. Crucially, this applies to the 24-hour rule: multiple smaller transactions from the same source within 24 hours that add up to $10,000 must be aggregated and reported as a single event.
- What is the "Travel Rule" for crypto in Canada?
The Travel Rule says that MSBs must get and send key information about the sender and receiver for any crypto transfer of $1,000 CAD or more. You need to make sure this data goes with the transaction to the receiving VASP. This requires special compliance protocols.
- How long does the Canada MSB registration process take?
Compared to the US or EU, Canada is efficient. Once you submit a complete application with FINTRAC, the registration can often be finalized within 2 to 4 weeks. The preparation phase usually takes 1 to 2 months. This includes incorporating your company and drafting your required AML policies before you can apply.
- Can a foreign company register as a Canada MSB?
Yes. You do not need to live in Canada to register. Foreign entities that market to Canadian clients, offer services in CAD, or target the Canadian market must register as a Foreign Money Services Business (FMSB). FMSBs face the exact same AML and reporting compliance requirements as domestic MSBs.
- Why do I need KYT software if I already have KYC?
KYC (Know Your Customer) only verifies identity (ID checks). KYT (Know Your Transaction) verifies the funds. By 2026, you must check wallet addresses. This ensures that funds don’t come from sanctions lists, hacks, or darknet markets. Without automated KYT software like Phalcon Compliance, you can't spot these risks manually. This leaves your business open to asset freezes.




