Think about a common scenario: your crypto exchange compliance stack looks “complete” on paper, but fails in the real world. You pass KYC (Know Your Customer), yet dirty funds slip in through bridges. You follow AML (Anti-Money Laundering), yet regulators demand proof, not promises. That gap creates frozen accounts, delayed approvals, and board-level pressure. It is a real Crypto Exchange Compliance risk: you can’t see danger early enough, thereby unable to defend your decisions clearly enough.
This is where compliance technology like Phalcon Compliance comes in. It fixes this by turning compliance into real-time control. You can get address screening, live transaction monitoring, and customizable risk engines that match different rules across markets. When alerts hit, you trace fund flows with MetaSleuth and export STR/SAR in one click, so you stay calm, clean, and compliant while users keep trading.
What Is Crypto Exchange Compliance?
Crypto exchange compliance is simply the set of rules a platform must follow to operate legally and safely. You know how banks have to check who you are and watch where your money goes. Crypto exchanges must do the same thing, but in the world of digital money. It’s not just about letting you trade Bitcoin or Ethereum. It’s about protecting users, stopping criminals, and obeying laws around the world.
The Regulatory Foundations
If you want to understand crypto exchange compliance, you need to know the foundation it stands on.
1. KYC(Know Your Customer)
The first layer is KYC, or “Know Your Customer.” When an exchange asks for your ID, a selfie, or proof of address, it is not being nosy. It aims to build a legal record of who is using the platform. Regulators expect exchanges to verify real identities, not just email addresses. Without KYC, bad actors can open unlimited accounts, move stolen funds, and disappear. With KYC, there is at least a traceable link between a wallet and a real person.
2. AML(Anti-Money Laundering)
The second layer is AML, or Anti-Money Laundering. This is where monitoring happens. Exchanges must watch transaction patterns, flag suspicious behavior, and file reports when needed. If large amounts of funds move through high-risk wallets or sanctioned addresses, the system must react. AML is not about blocking normal users, but detecting abnormal patterns before they grow into systemic risk.
3. FATF (the Financial Action Task Force) and Travel Rule
Above these rules sits FATF. This global body is built to set the standards that countries follow. One key FATF rule is the Travel Rule, or the Recommendation 16 of the FATF’s 40 Recommendations. It requires exchanges to attach sender and receiver information when crypto moves between platforms above certain thresholds. In simple terms, crypto transactions between exchanges can no longer be anonymous at scale.
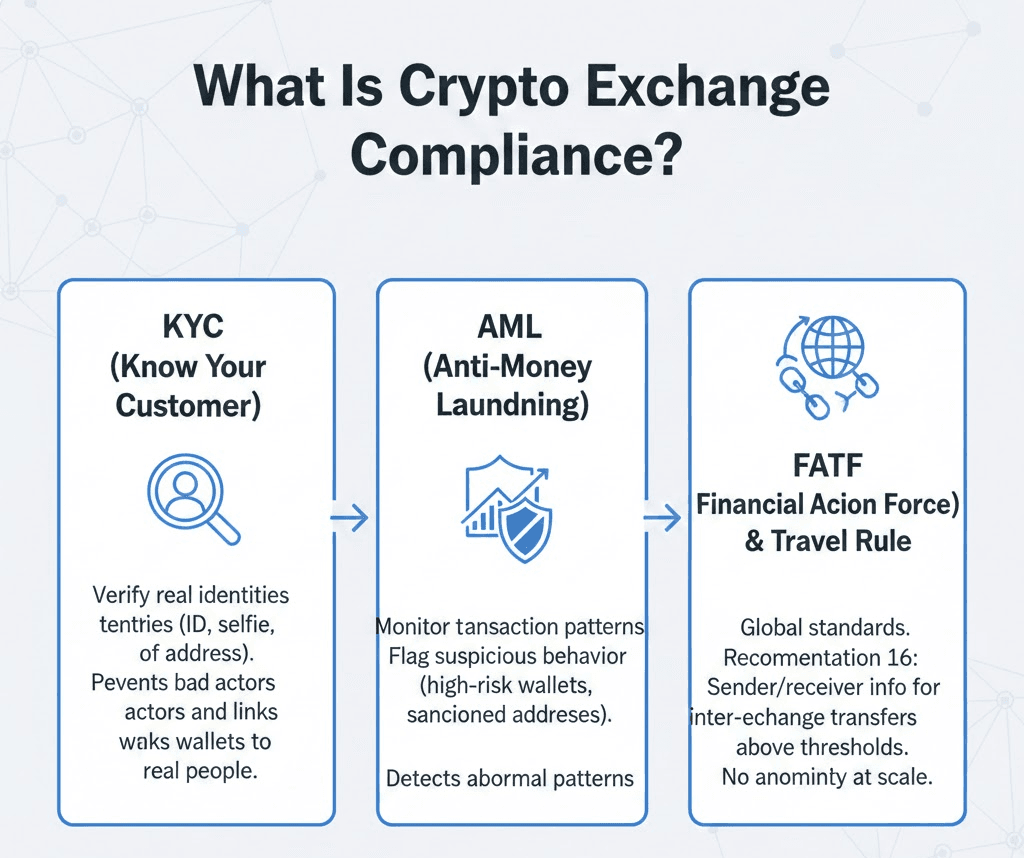
Together, KYC, AML, FATF guidance, and the Travel Rule form the legal backbone of crypto exchange compliance. They turn an exchange from a simple trading website into a regulated financial gatekeeper.
Crypto Exchange Compliance Is Shifting
From "Who Are You?" to "Where is the Money?"
When you sign up for a crypto exchange, they always ask for your ID and a selfie. For a long time, people thought that was the only rule in crypto exchange compliance. But guess what? Knowing who you are doesn't stop an exchange from losing your money or lying about their vault.
Here is the big secret: True compliance has moved past just checking your name. It’s now about Asset Monitoring. It’s like a bank having a glass wall where you can see the money sitting in the safe at any time. The old way of exchanges is more like "Trust us, we have your coins.". And you just hope they are telling the truth. But now, you can see the digital trail. You check their "Proof of Reserves" to make sure your Bitcoin is actually there.
Why should you care? Because if an exchange only does KYC but hides what they do with your money, you could lose everything overnight, just like what happened with FTX. We are moving to a world where "Don't Trust, Verify" isn't just a cool saying; it’s the new legal law.
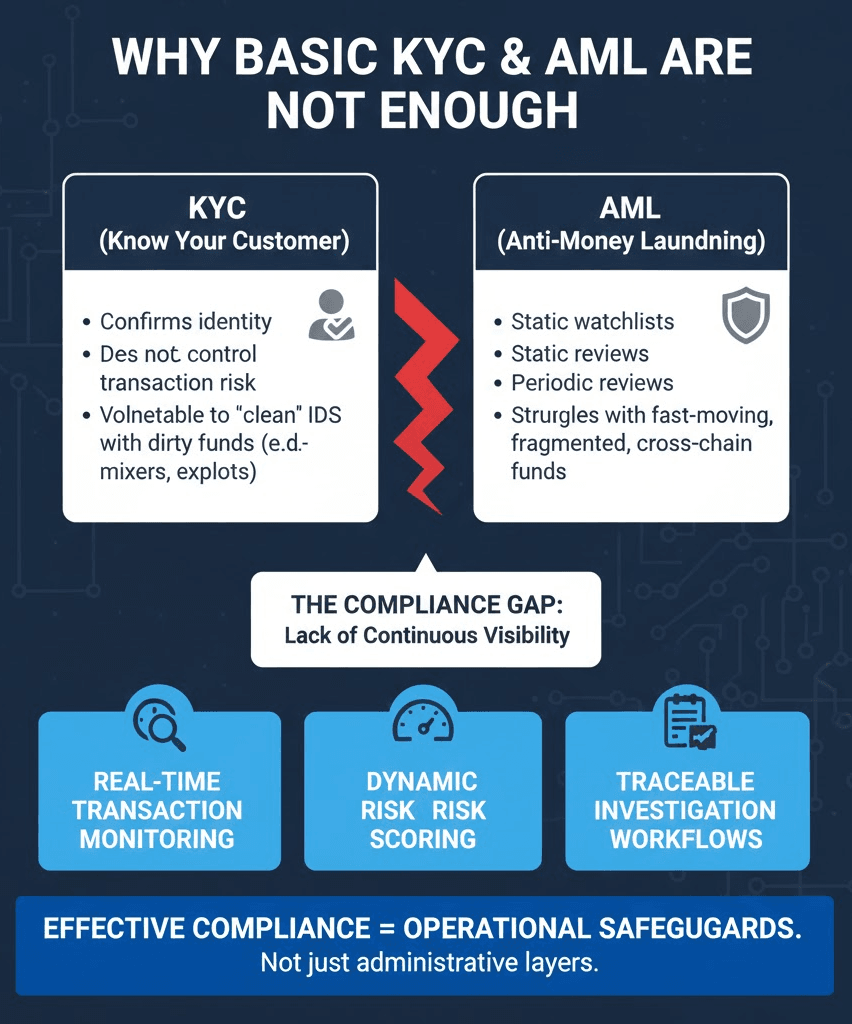
Why KYC and Basic AML Are Not Enough
KYC confirms identity, but identity alone does not control transaction risk. A user can pass document verification and still deposit funds that recently moved through a bridge exploit, a mixer, or a sanctioned cluster. In crypto exchange compliance, the real exposure often sits in the fund flow, not the profile.
Basic AML setups typically rely on static watchlists and periodic reviews. These controls can detect known high-risk addresses, but they struggle with fast-moving threats. Illicit actors fragment funds across multiple wallets, move assets cross-chain, and re-enter platforms through newly created addresses. By the time a blacklist updates, the funds may already be credited or withdrawn.
Regulators increasingly expect more than identity checks and reactive reporting. They expect exchanges to demonstrate how suspicious activity was identified in context, how risk was assessed, and what action was taken in real time. If compliance teams cannot reconstruct transaction paths, explain exposure depth, and provide structured decision logs, the platform is seen as weakly controlled.
The gap is not a lack of policy. It is a lack of continuous visibility. Effective crypto exchange compliance requires real-time transaction monitoring, dynamic risk scoring, and traceable investigation workflows. Without these, KYC and basic AML become administrative layers rather than operational safeguards.
Where Crypto Exchange Compliance Commonly Breaks Down
Compliance failures often occur when screening is limited to static lists. Illicit actors move funds quickly across bridges, mixers, and newly created wallets. Without real-time monitoring and fund tracing, exposure may be detected too late or not at all.
Regulatory penalties are frequently triggered by insufficient documentation. Authorities expect exchanges to demonstrate how suspicious activity was identified, assessed, and reported. If reporting workflows are manual or inconsistent, this increases regulatory risk.
Bridge-related laundering creates additional complexity. Attackers use cross-chain transfers to fragment transaction history. Without path-level tracing tools such as MetaSleuth, identifying indirect exposure becomes operationally difficult.
Banking disruptions typically arise when financial partners lose confidence in monitoring standards. Exchanges that cannot demonstrate structured AML/CFT controls, real-time detection, and documented reporting processes may face service restrictions.
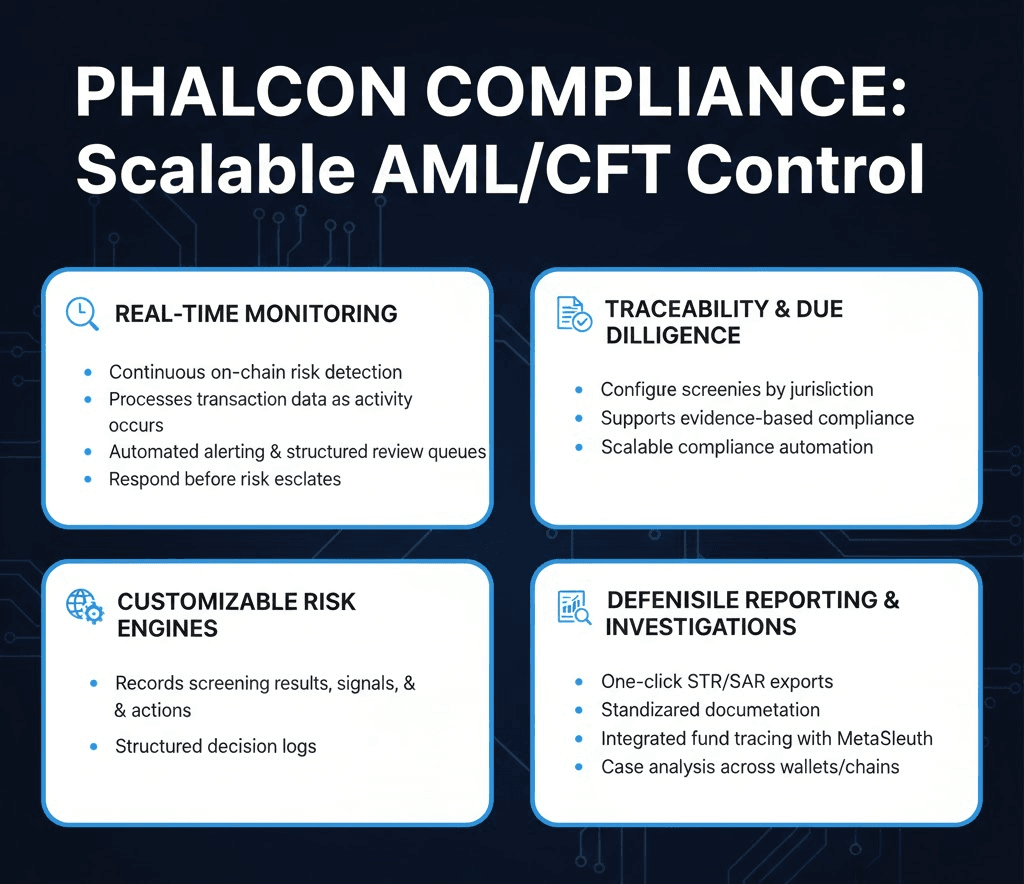
How Phalcon Compliance Enables Scalable AML/CFT Control
Real-time monitoring requires continuous on-chain risk detection. Phalcon Compliance processes transaction data as activity occurs, supporting operational controls such as automated alerting and structured review queues. It allows teams to respond before risk escalates.
Demonstrating reasonable due diligence depends on traceability. Phalcon Compliance records screening results, monitoring signals, and response actions. It supports evidence-based compliance operations rather than informal decision-making.
For organizations operating across markets, compliance obligations differ by jurisdiction. Customizable risk engines allow teams to configure rules aligned with regional AML/CFT requirements, supporting scalable compliance automation without rebuilding workflows for each market.
Reporting must be efficient and defensible. With one-click STR/SAR exports, Phalcon Compliance simplifies suspicious activity reporting. It helps teams generate standardized documentation directly from monitored activity and investigation results.
For deeper case analysis, MetaSleuth integrates fund tracing into compliance workflows. This enables exchanges and crypto payment platforms to follow illicit activity across wallets and chains while maintaining structured case records.
Use Cases in Practice
For crypto payment platforms, Phalcon Compliance supports real-time detection of high-risk deposits, prevents risky withdrawals, and simplifies reporting through integrated STR/SAR export workflows.
For centralized exchanges, it enables scalable AML automation with customizable risk engines and provides investigation capabilities through MetaSleuth to trace suspicious fund movements efficiently.
Crypto exchange compliance today is not defined by policies alone. It depends on continuous monitoring, configurable risk logic, structured investigations, and defensible reporting. Phalcon Compliance provides the operational framework to support AML/CFT obligations in real time while maintaining scalable control.
Conclusion: Compliance is Your "Safety Vest"
Why a "Strict" Exchange is Actually Your Best Friend
It’s easy to get annoyed when an exchange asks for your ID or blocks a suspicious trade. But remember: Compliance is a Moat. A "Good Exchange" uses compliance to build a wall around your money. It keeps out the hackers, it keeps out the scammers, and it keeps the exchange from being shut down by the government. In the world of crypto, crypto exchange compliance is no longer about paperwork. It is about survival. From a user’s point of view, good crypto exchange compliance means three simple things:
- Your money is separate from their money.
- They can prove they actually have your coins.
- They are playing a fair game, not a rigged one.
FAQ
If a crypto exchange is “compliant,” why can accounts still get frozen without warning?
Compliance does not mean “no freezes.” In practice, compliant exchanges are required to act before regulators or banks step in. If a transaction triggers risk signals, such as links to sanctioned wallets, hacked funds, or suspicious cross-chain activity, the exchange may temporarily freeze the account to investigate. This is not arbitrary control. But rather, it’s a defensive move to prevent the entire platform from being flagged or cut off by banks. In other words, account freezes are often a byproduct of compliance, not a failure of it.
Why do compliant exchanges delist coins that are still trading fine elsewhere?
Because compliance is jurisdiction-specific. A token that is legally tradable on one platform may be considered a security, unlicensed stablecoin, or high-risk asset in another region. Under frameworks like MiCA (Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation) in Europe or SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission) enforcement in the US, exchanges are held responsible for the legal status of listed assets. When a compliant exchange delists a token, it is often reducing legal exposure, not making a judgment on the token’s popularity or price potential.
Does crypto exchange compliance mean my on-chain privacy is gone forever?
Not necessarily. While compliant exchanges must collect identity data to meet AML and tax requirements, privacy laws such as GDPR restrict how long data can be stored, how it can be used, and who can access it. Many modern compliance systems aim to minimize data retention and separate identity checks from transaction monitoring. Compliance reduces anonymity, but it does not automatically mean unlimited surveillance. How data is handled matters as much as what is collected.
Why do compliant exchanges treat cross-chain transfers as “high risk”?
Because cross-chain bridges are one of the most abused tools in crypto crime. Hackers frequently move stolen funds across chains to break transaction trails. As a result, compliance systems flag bridge-related activity more aggressively than single-chain transfers. Even if your funds are legitimate, using a bridge shortly after a known exploit can cause temporary restrictions. This is why compliant exchanges increasingly analyze transaction context, not just wallet ownership.
How do compliant exchanges actually tell “clean users” from hackers in real time?
Modern crypto exchange compliance does not rely on manual reviews or delayed investigations. Instead, advanced exchanges use real-time on-chain monitoring tools such as Phalcon Compliance to analyze transaction behavior as it happens. These systems do not simply check wallet addresses against blacklists. They examine execution patterns, fund flow paths, and cross-chain movement behavior to identify whether a transaction matches known attack or laundering signatures. This allows compliant exchanges to stop truly malicious activity before funds are fully withdrawn, while reducing false positives that freeze legitimate users. The goal is not mass surveillance, but early risk detection without punishing normal users after the fact.




